Accuracy
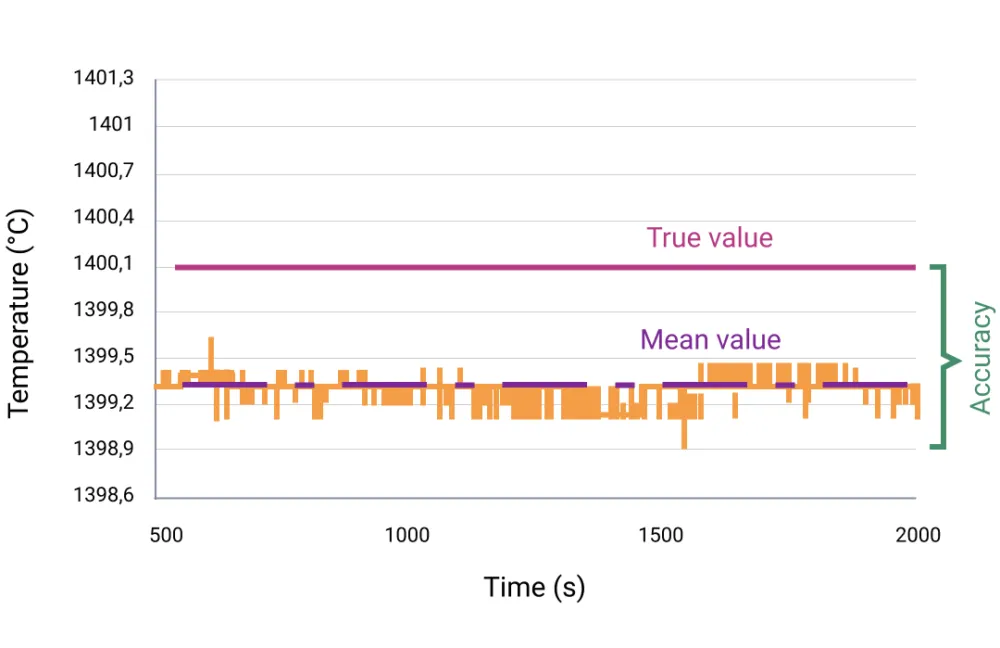
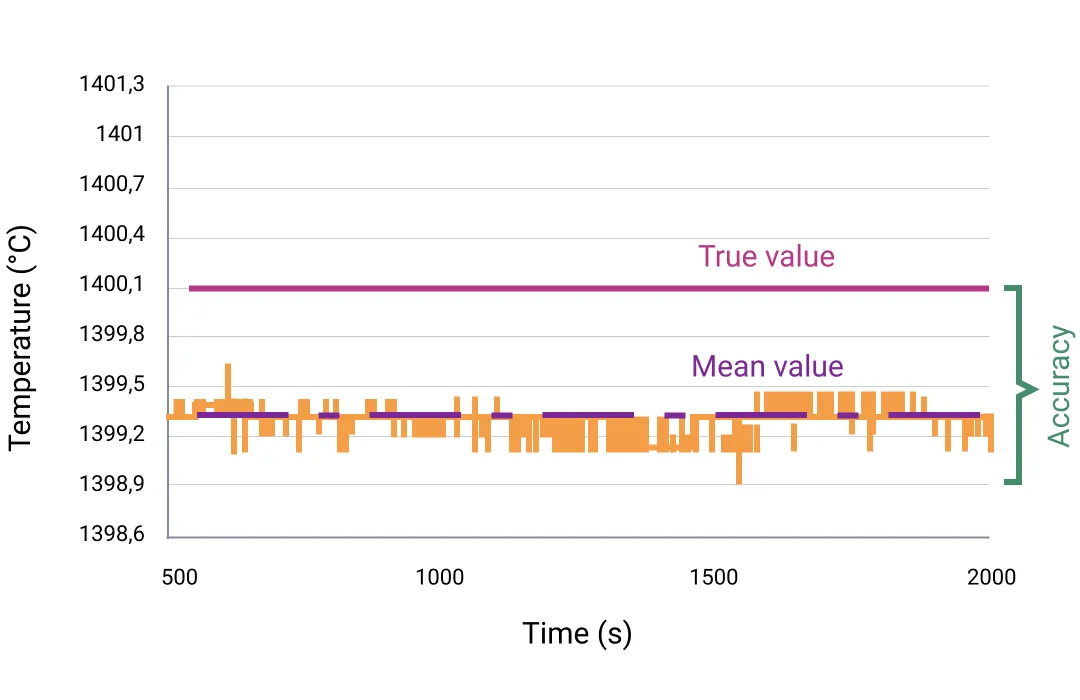
Accuracy, as a device specification, indicates how closely measured values align with the true value. This makes it one of the most important properties of a measuring device.
The true temperature value can only be reliably determined using a transfer standard traceable to the international temperature scale. This could be a pyrometer calibrated by a national metrological institute (such as the Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt in Germany) or an accredited laboratory. Every measurement has a certain degree of uncertainty, caused by factors like signal noise. Therefore, accuracy is expressed statistically. Typically, measuring accuracy is stated as: (+/- 1K, k = 2).
This means that with 95% probability (k = 2 indicates twice the standard deviation or confidence interval), a measured value may deviate by a maximum of 1 K without violating the specification. A statement such as (+/- 1K or +/- 1% of the measured value in °C – whichever is larger) may also be used. This means that a measuring accuracy of 1 K applies for temperatures up to 100 °C and 1% for temperatures above this. For an object at 500 °C, measured values between 495 °C and 505 °C are acceptable.
However, measurement accuracy is only meaningful if additional information clarifies the conditions under which the device specification applies. Common information includes the emissivity of the measurement object, measurement geometry (distance, object size), integration time, and ambient temperature.
Back to LexiconRecommended Products

Talk to us about your IR Temperature Measurement Requirements
Our Infrared Temperature Measurement experts can help you find the right Optris product for your application.